Worst-case performance:
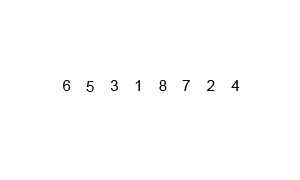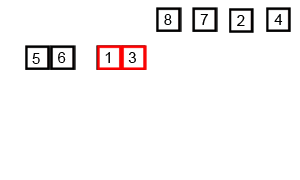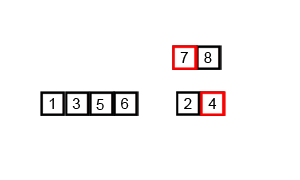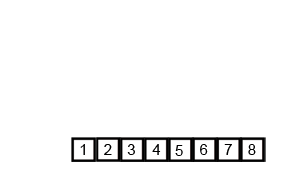
Merge sort operates by recursively splitting the list into half until it is divided into the smallest possible unit, then merging them together while sorting them.
Python Implementation:
def mergesort(list):
if len(list) <= 1:
return list
mid = len(list) // 2
left = list[:mid]
right = list[mid:]
left = mergesort(left)
right = mergesort(right)
return merge(left, right)
def merge(left: list, right: list):
result = []
finallen = len(left) + len(right)
while len(result) < finallen:
if len(left) == 0:
result += right
break
if len(right) == 0:
result += left
break
if left[0] < right[0]:
result.append(left[0])
left.pop(0)
else:
result.append(right[0])
right.pop(0)
return resultAlternatively:
# MODE : "asc" or "desc"
def sort(input:list, mode:str) -> list:
lengh = len(input)
if lengh <= 1:
return input
middle_index = lengh//2
leftList=input[:middle_index]
rightList=input[middle_index:]
sortedLeftList = sort(leftList,mode)
sortedRightList = sort(rightList,mode)
lLengh = len(sortedLeftList)
rLengh=len(sortedRightList)
result=[]
li,ri=0,0
for i in range(lengh):
if li >= lLengh:
result.append(sortedRightList[ri])
ri+=1
continue
if ri >= rLengh:
result.append(sortedLeftList[li])
li+=1
continue
priority=""
if mode =="asc":
if sortedLeftList[li] > sortedRightList[ri]:
priority = "r"
else:
priority="l"
elif mode =="desc":
if sortedLeftList[li] < sortedRightList[ri]:
priority = "r"
else:
priority="l"
if priority=="r":
result.append(sortedRightList[ri])
ri+=1
continue
else:
result.append(sortedLeftList[li])
li+=1
continue
return result