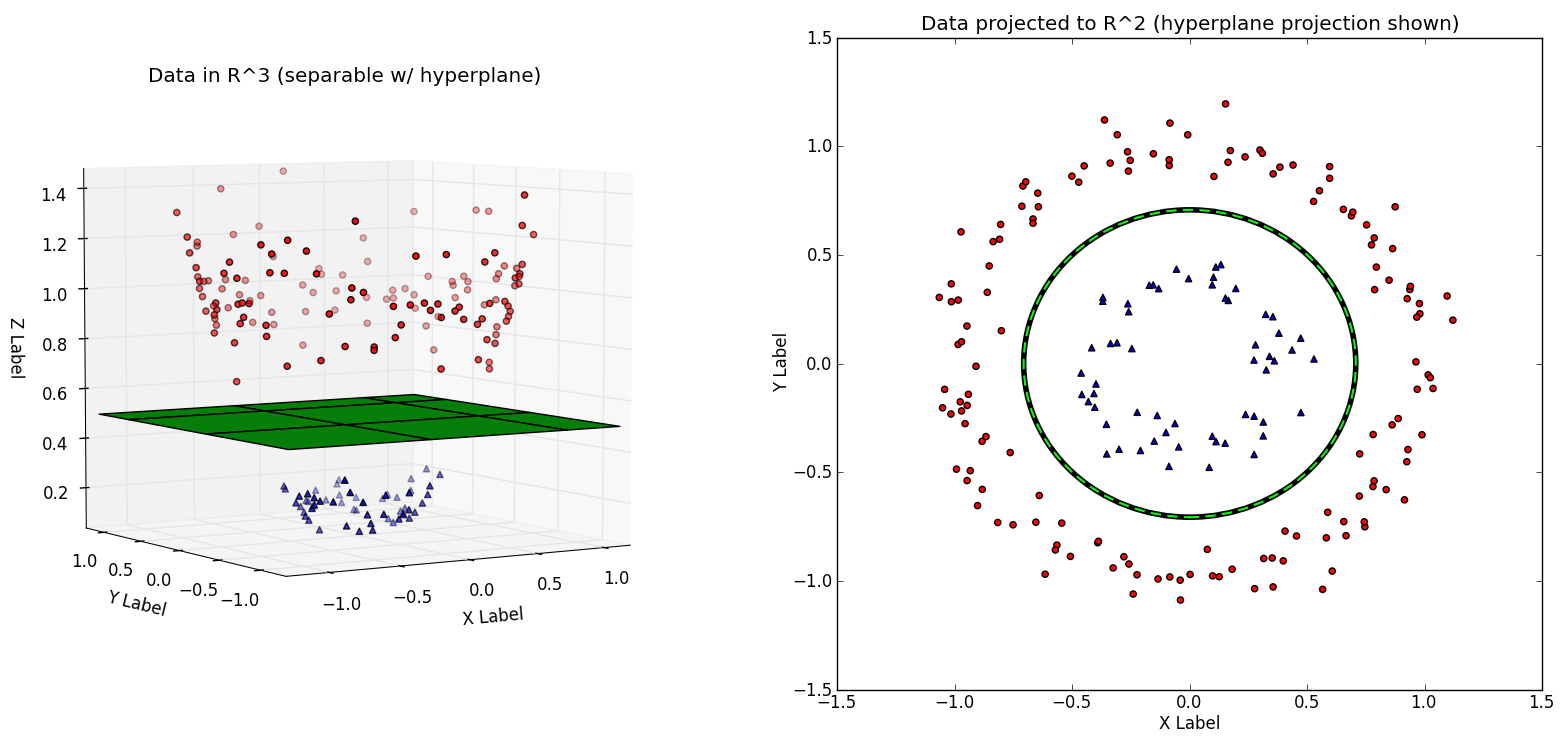
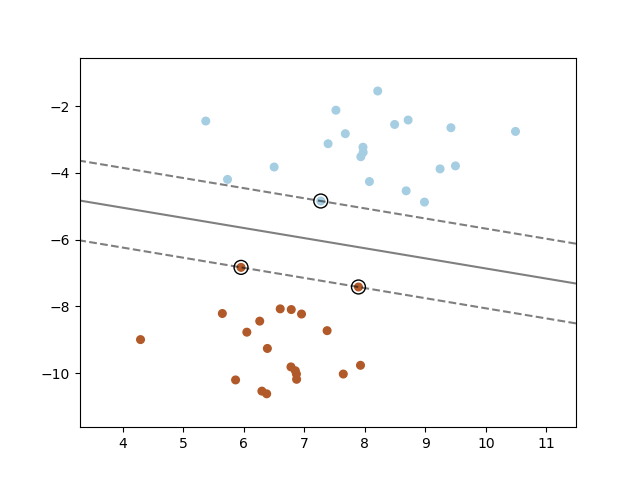
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are supervised learning models that classify a set of data. SVMs aim to find the optimal hyperplane, which is a decision boundary separating the classes, such that the distance from the hyperplane to the nearest data point on each side is maximised. This hyperplane is called the maximum-margin hyperplane, and the classifier it produces is called the maximum-margin classifier. The data points closest to the decision boundary are called “support vectors”.
In cases where data cannot be classified, such as 1D data, a kernel can be applied to transform the data, so that a hyperplane through the transformed data can separate it.